Baltimore Classification

The baltimore classification is based on genetic contents and replication strategies of viruses.
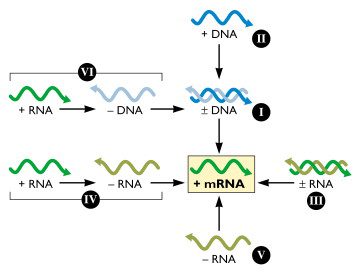
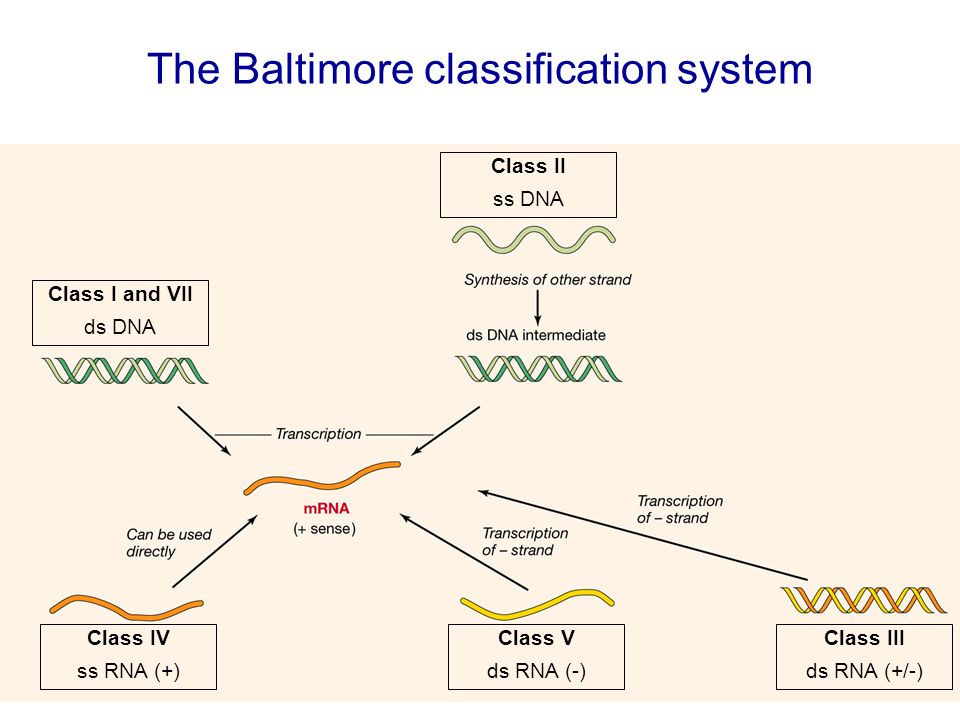
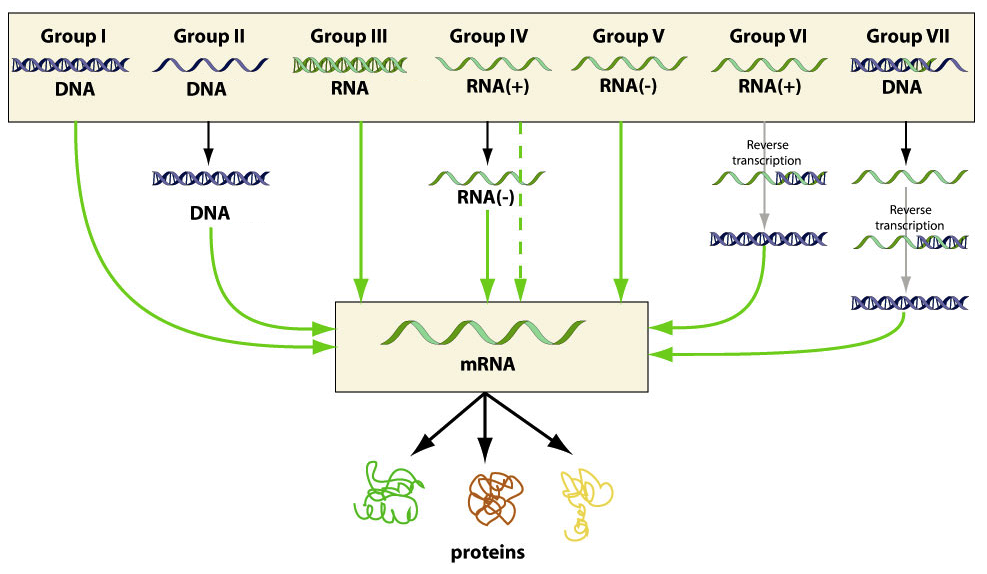
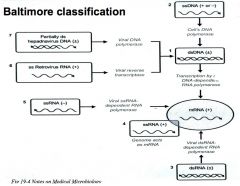
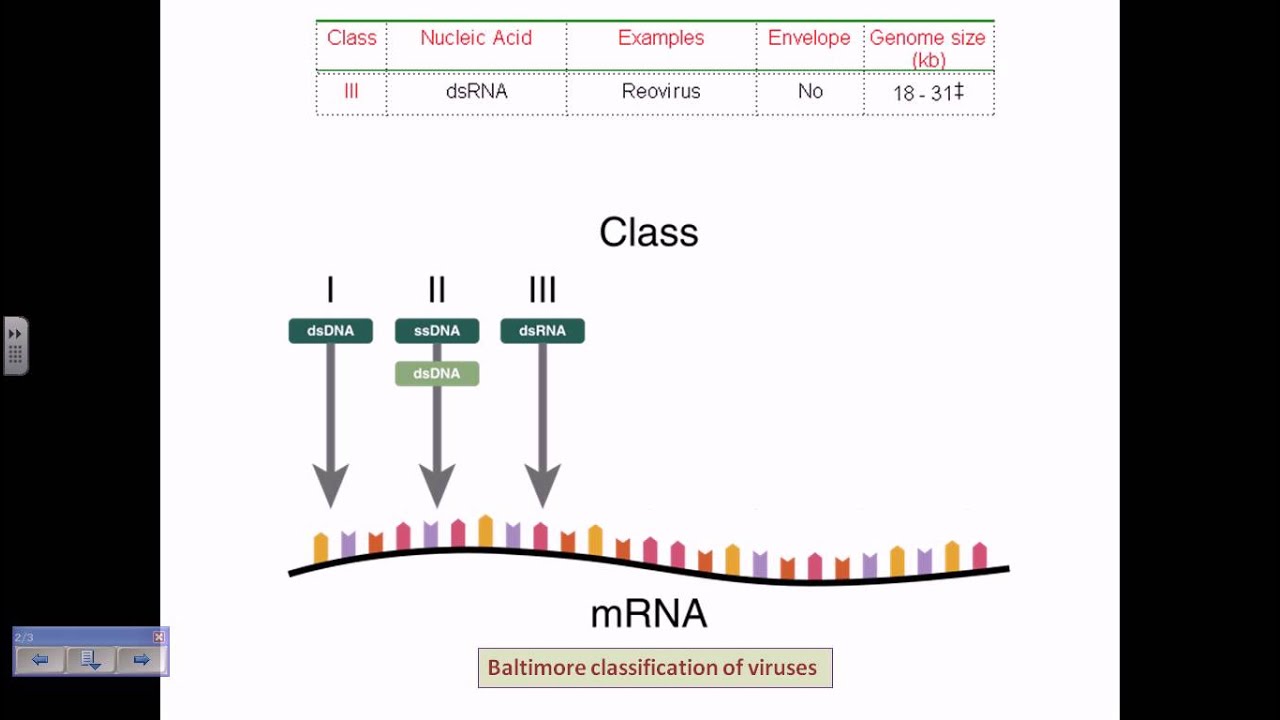
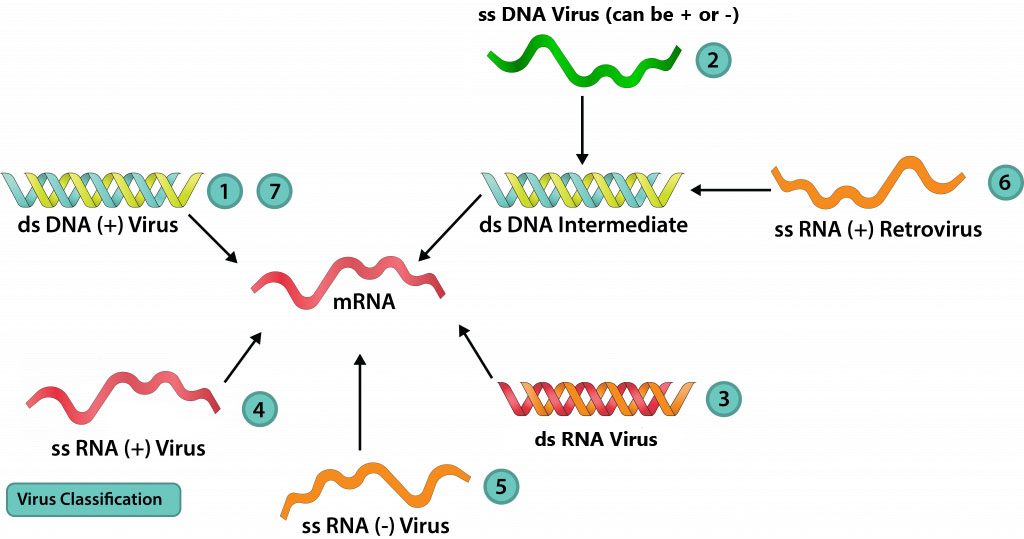
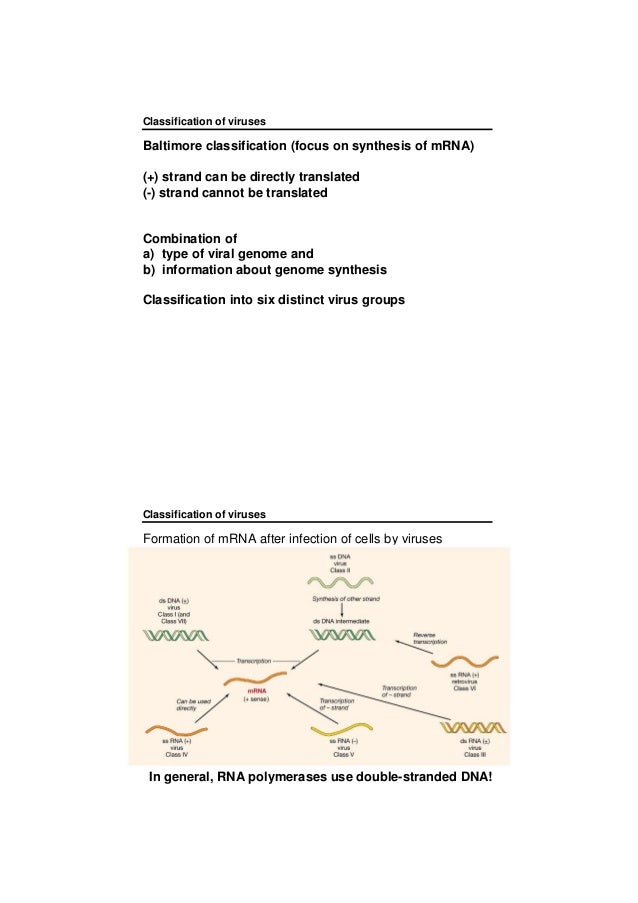
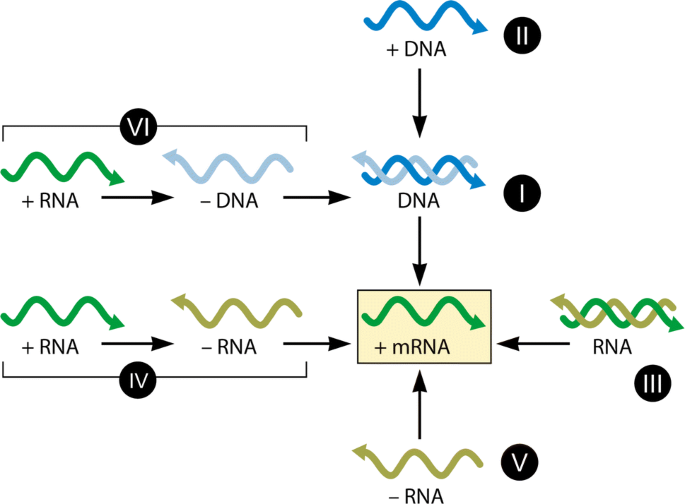
Baltimore classification. The central theme of the baltimore system of virus classification is all viruses must synthesize positive strand mrnas from their genomes in order to produce proteins and replicate themselves the precise mechanisms whereby this is achieved. The baltimore classification system is a scheme for classifying viruses based on the type of genome and its replication strategy. Supplement viruses may be classified as follows according to their type of genome.
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger rna mrna synthesis. The genetic material in all types of cells is double stranded dna but some viruses use rna or single stranded dna to carry genetic information. Definition noun a classification system for viruses according to their type of genome dna rna single stranded ss double stranded ds etc and their method of replication.
The system was developed by david baltimore. The baltimore system of virus classification devised by virologist nobel laureate david baltimore is based on the genomic nature of the viruses. In addition to the differences in morphology and genetics mentioned above the baltimore classification scheme groups viruses according to how the mrna is produced during the.
Baltimore classification the most commonly used system of virus classification was developed by nobel prize winning biologist david baltimore in the early 1970s. Baltimore classification first defined in 1971 is a classification system that places viruses into one of seven groups depending on a combination of their nucleic acid dna or rna strandedness single stranded or double stranded sense and method of replication. Named after david baltimore a nobel prize winning biologist these groups.
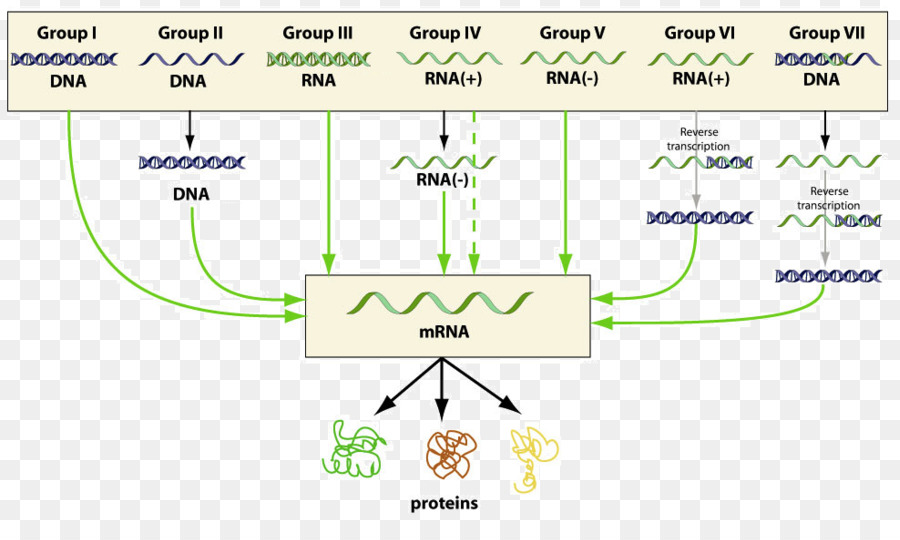
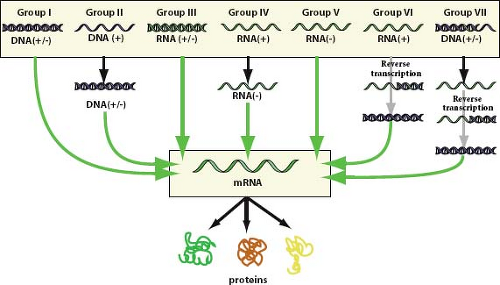
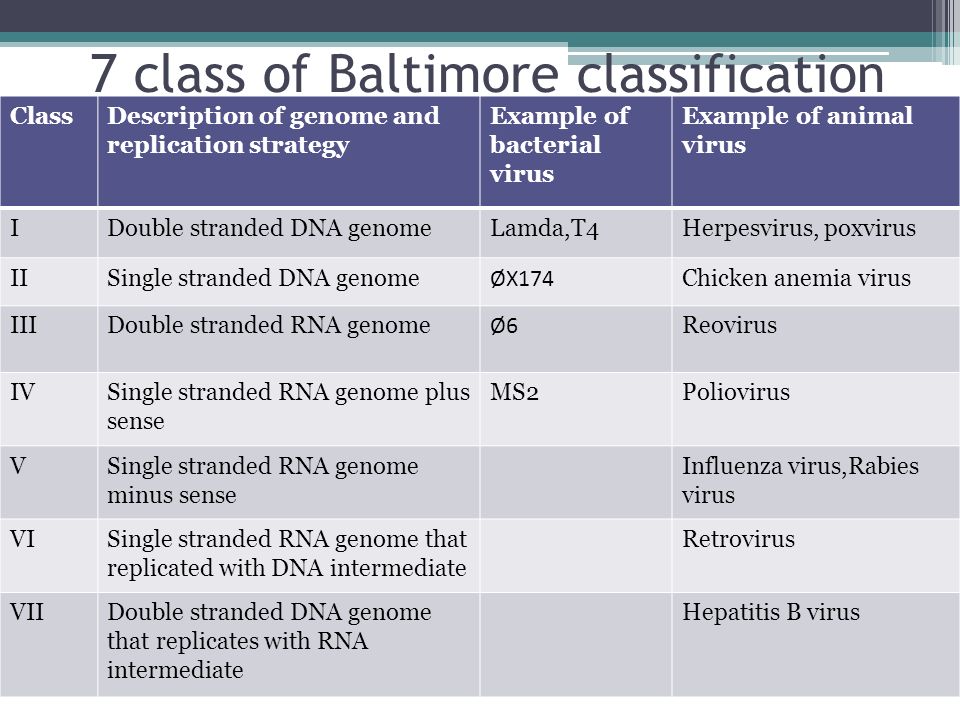
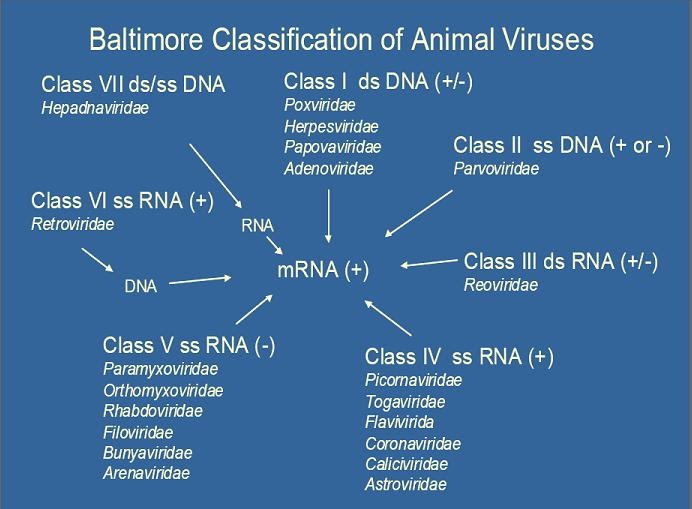
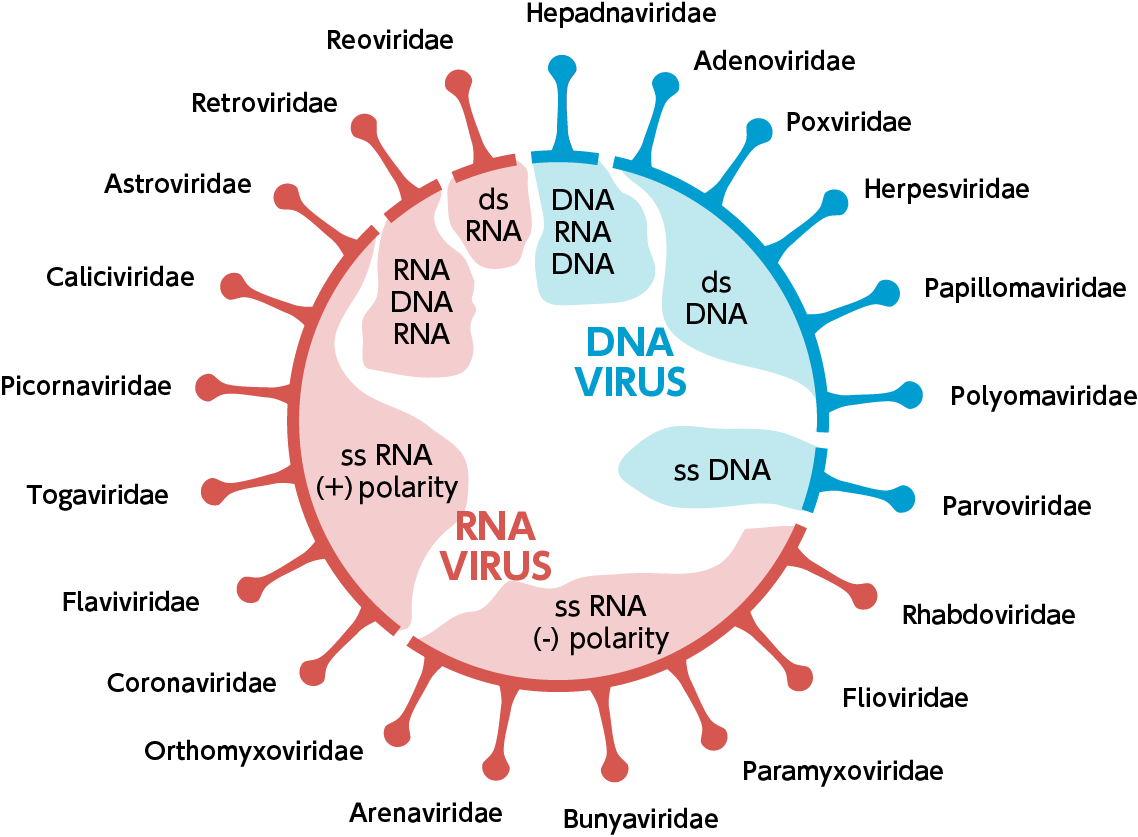
According to baltimore classification viruses are divided into the following seven classes. As such there are seven groups of classification. The baltimore classification developed by david baltimore is a virus classification system that groups viruses into families depending on their type of genome dna rna single stranded ss double stranded ds etc and their method of replication.
This kind of viral classification was created by an american biologist named david baltimore. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mrna production it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Baltimore classification first defined in 1971 is a classification system that places viruses into one of seven groups depending on a combination of their nucleic acid dna or rna strandedness single stranded or double stranded sense and method of replication.
Groups i vii.